 |
From citation to full-text: an integration aid to facilities for retrieving documents indexed by PUBMED. Maurella Della Seta*, C. Di Benedetto**, A. Dracos*, G. Poppi***
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to show
an interface, developed by Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS), for
connection between journals indexed by PubMed and Italian libraries holdings,
finalized at retrieving the original document on a national or international
basis.
Introduction In recent literature many studies analyzed behavior of researchers and the way in which they prefer to retrieve publications they need. There is an increased feeling, among end-users, that everything can be get on the Internet and "a clear trend, for young researchers in particular, is to go around subscription barriers (both for paper an electronic material) and rely almost exclusively on what they can find free on the Internet, which often include working versions posted on the home pages of authors". But few items are available free-of-charge on the Net, and the expectations of end-users are often disappointed. The spreading of free databases on the Web, which are being searched by millions of scientists and laymen, nowadays emphasizes the importance of retrieving the full text. In spite of so many tools available, (e.g. OPACS, serials directories, publishers'web sites), retrieval of full-text is still difficult and has to face a variety of fees and ways of accessing, often not so easy to find. In consideration of the electronic media potentialities end-user's expectations should be better satisfied. As the Internet and World Wide Web
created a rich environment for the creation, organization and dissemination
of information, one of the main tasks of librarians became the organization
of knowledge, which will continue to be "a central issue for those in library
and information science who have been dealing with this problem for years".
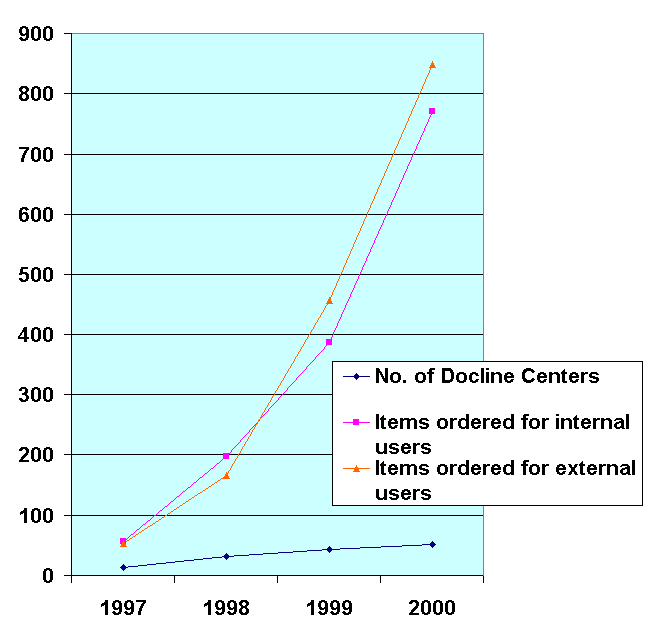
Role of the Istituto Superiore di Sanità in document delivery The Istituto Superiore di Sanità (Italian National Institute of Health) is a technical scientific organism of the Italian National Health Service. The Documentation Service supports ISS research by providing technical and scientific information through online information retrieval and searching. It is also the only national center for DOCLINE, the NLM system for full-text retrieval; it acts as a focal point by collecting orders of articles not available in Italian libraries, and forwarding them to NLM via the Internet. In the light of the free availability of PubMed on the Web, the number of items ordered to NLM for internal (ISS) and external Italian users has considerably increased (see figure 1). During the year 2000 an overall amount of 1619 items were ordered to NLM, of which 1425 received.
The ISS Library is specialized in scientific documentation in biomedical and public health-related fields and owns over 2000 current periodicals, of which more than 500 available both in print and in electronic format. Document delivery is limited to Italian libraries or documentation centers, according to mutual agreements. Analyzing the requests of ISS internal and external patrons, it was assumed that the Italian scientific community needed a single interface to easily assess: On the basis of these premises, we developed a searching tool, aimed at the organization and the integration of facilities available for retrieving journal articles indexed by PubMed, produced by the US National Library of Medicine. Methods Through the collaboration of the ISS Electronic Data Management Service, an interface has been developed, hosted by a database on a SQL 7.0 server, while the software ACCESS is employed as a client, with the purpose of ensuring patrons optimal access to available resources. As a first step, two data sets were downloaded from NLM Web site: the List of Serials Indexed for Online Users 2000 and the List of Journals Indexed in Index Medicus 2000, both in Portable Document Format (PDF). The List of Serials Indexed for Online Users is designed to provide bibliographic information for serials cited in MEDLINE: citations for these serials date back as far as 1966 and include serials formerly found in the separate NLM databases HealthSTAR and AIDSLINE. It contains 9,613 serial titles, including 4,514 titles currently indexed for MEDLINE, as of December 2000. This list was converted from PDF format in Word format and later in text format: relevant fields (Title, Medline abbreviation and International Standard Serial Number) were imported in our ACCESS database, making up the first part of the record (see figure 2). These above-mentioned fields also are the main access keys in the user searchable interface. The second part of the record aims at ensuring access to resources available at a local (ISS Library), national and international level. For this purpose the following links have been established to: the electronic catalogue of the ISS Library, which has been using the DOBIS-LIBIS system for twenty years. DOBIS-LIBIS allows automatic serials management and record-keeping: patrons may therefore verify the presence of a specific item, timely checking the actual availability of every serial issue; the Italian Periodicals Catalogue (ACNP), for identification of Italian libraries which hold the journal. This catalogue contains the serial holdings of over 2300 libraries, in all subject fields. Links from journals indexed in PubMed and ACNP have been automatically established through the ISSN; The third part of the record allows subject approach to serials. Each periodical will be indexed in Italian, using the Italian translation of Medical Subject Headings, prepared by ISS. The indexing scheme adopted by the List of Journals Indexed in Index Medicus has been used for the 3,559 journals currently indexed for Index Medicus. For the remaining 6,054 titles, considered only in the List of Serials Indexed for Online Users but not in the List of Journals Indexed in Index Medicus, indexing by Italian MeSH translation is in progress.
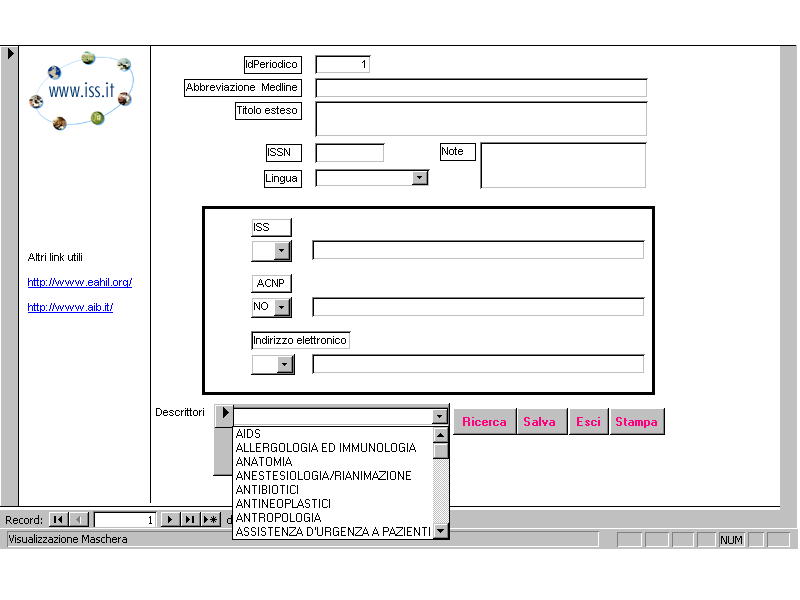 [click on the image to enlarge it] Conclusions By searching the database, via Intranet for ISS staff and via the ISS Web site for the other Italian users, patrons will check the availability of a journal in Italy, and consequently decide which steps have to be taken for its retrieval. A special value will be added by Italian indexing, which will help users in retrieving journals in the same subject field. As a future implementation, the file
could be uploaded directly into PubMed, in the special area provided by
NLM for library holdings (Cubby), which at present is open only to U.S.
libraries. The transfer into PubMed will offer an easier access by granting
an immediate and direct orientation to Italian users.
References 1. Bjork, B.C. and Turk, Z. - How Scientists Retrieve Publications: An Empirical Study of How the Internet
Is Overtaking Paper Media. The Journal of Electronic Publishing. 6 (2)
December, 2000. (http://www.press.umich.edu/jep/06-02/bjork.html
|
|
|
|
|