 |
|
When :
Brief history
-
August 1998 - Ovid Web Gateway test
begins in Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine (IKEM)
-
January 1999 - 15 institutions are connected,
user guide is translated and adapted
-
January 2000 - 20 institutions
-
August 2000 - experimental online tutorial
is launched
-
January 2001 - 23 institutions + 9 trials
(923 userIDs)
What : Databases
-
Bibliographic : Medline, HealthStar,
Cinahl, Embase: Drugs & Pharmacology, Current Contents
-
Fulltext: Core Biomedical Collection
-
Evidence Based Medicine: Best Evidence,
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Who : Consortium Members
| |
Number of UserIds |
| Teaching Hospital Bulovka Prague |
43 |
| Teaching Hospital Royal Vineyards
Prague |
117 |
| Teaching Hospital Ostrava |
1 |
| St Anne University Hospital Brno |
3 |
| Teaching Hospital Pilsen |
55 |
| Teaching Hospital Hradec Kralove |
23 |
| Teaching Hospital Olomouc |
3 |
| Teaching Maternity Brno |
12 |
| Institute of Physiology Prague |
50 |
| Institute for Clinical and Experimental
Medicine Prague |
7 |
| Masarik Hospital Ustinad Labem |
1 |
| Masarik Memorial Cancer Institute
Brno |
20 |
| National Medical Library Prague |
1 |
| Hospital Ceske Budejovive |
3 |
| Na Homolce Hospital Prague |
4 |
| State Silesian Hospital Opava |
1 |
| Institute of Hematology and Blood
Transfusion Prague |
51 |
| General Teaching Hospital Prague |
267 |
| General Hospital Nachid |
1 |
| Institute for Child Health Brno |
1 |
Added value : Czech user documentation
-
Complete Czech documentation in various
formats - quick reference card, user guide, "How to..."
-
Brief online tutorial. This interactive
"demoversion" with comments should serve as an introduction to Ovid.
-
Other online interactive materials.
A complete Czech online course of Ovid searching for both librarians and
physicians is being prepared.
-
Regular user meetings with Ovid sales
manager for Central & Eastern Europe, that are intended for presenting
new developments.
-
Surveys.
Results : A little bit of
statistics
Figure 1.
Aggregate database
usage 1999 - 2000
| |
Total |
Average per Session |
| Search Session |
20747 |
|
| Session Lenght in Minutes |
313130 |
15,093 |
| Search Statements |
137011 |
6,604 |
| Records Viewed |
186289 |
8,979 |
| Full Text Document Viewed |
10226 |
0,493 |
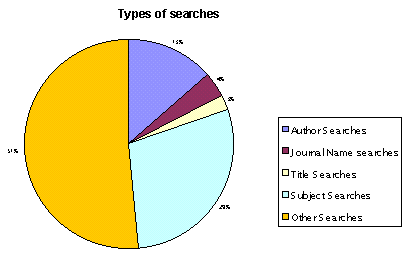
| Authors Searches |
18236 |
0,879 |
| Journal Name Searches |
5432 |
0,262 |
| Title Searches |
3435 |
0,166 |
| Subject Searches |
39621 |
1,910 |
| Other SEarches |
70287 |
3,388 |
Figure 2.
Individual database
usage
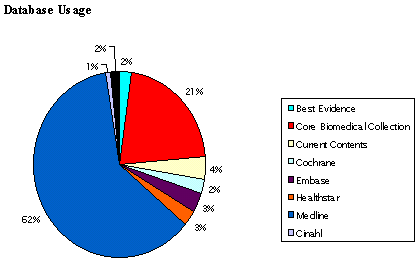
Figure 3. Average system load
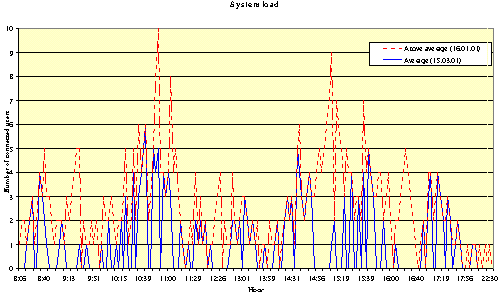
Figure 4.
Types of searches
Benefits
-
Financial savings. Although Ovid consortium
is not a proper consortium yet, it is considered as such and the licence
is cheaper.
-
Opportunity to access databases and
fulltext journals for smaller hospitals with limited funds. Some of the
connected institutions do not subscribe to any print foreign journals,
neither do they buy any databases.
-
Possibility of interlinking with other
projects through Ovid OpenLinks.
-
Promotion of end users' searching thanks
to user friendly interface
-
Promotion of Evidence Based Medicine
resources among Czech medical population.
Problems
-
Low usage (see Fig. 1 and 3) caused
by:
-
a lack of end user awareness. Ovid is
mainly used by librarians and information professionals, although it does
not require a lot of special searching skills. Medline is considered as
being a "gold standard" and other databases are used scarcely.
-
a low level of information literacy
among end users. Inefficient search strategies (Fig. 4) often cause disappointment
and frustration.
-
Financial uncertainty. The project has
no stable financial support, it is partly sponsored by Czech Ministry of
Health, partly from IKEM's sources.
-
A lack of feedback. From hundreds of
users only 18 responded to the online urvey.
-
Acquisition overlap. There are more
Medlines and Embases among consortium members, but this problem should
be eliminated in the near future by better acquisition coordination.
|